1
Learning Objectives
- Understand how official poverty in the United States is measured.
- Describe problems in the measurement of official poverty.
- Describe the extent of official poverty.
When US officials became concerned about poverty during the 1960s, they quickly realized they needed to find out how much poverty we had. To do so, a measure of official poverty, or a poverty line, was needed. A government economist, Mollie Orshanky, first calculated this line in 1963 by multiplying the cost of a very minimal diet by three, as a 1955 government study had determined that the typical American family spent one-third of its income on food. Thus a family whose cash income is lower than three times the cost of a very minimal diet is considered officially poor.
This way of calculating the official poverty line has not changed since 1963. It is thus out of date for many reasons. For example, many expenses, such as heat and electricity, child care, transportation, and health care, now occupy a greater percentage of the typical family’s budget than was true in 1963. In addition, this official measure ignores a family’s noncash income from benefits such as food stamps and tax credits. As a national measure, the poverty line also fails to take into account regional differences in the cost of living. All these problems make the official measurement of poverty highly suspect. As one poverty expert observes, “The official measure no longer corresponds to reality. It doesn’t get either side of the equation right—how much the poor have or how much they need. No one really trusts the data” (DeParle, et. al., 2011). We’ll return to this issue shortly.

The poverty line is adjusted annually for inflation and takes into account the number of people in a family: The larger the family size, the higher the poverty line. In 2010, the poverty line for a nonfarm family of four (two adults, two children) was $22,213. A four-person family earning even one more dollar than $22,213 in 2010 was not officially poor, even though its “extra” income hardly lifted it out of dire economic straits. Poverty experts have calculated a no-frills budget that enables a family to meet its basic needs in food, clothing, shelter, and so forth; this budget is about twice the poverty line. Families with incomes between the poverty line and twice the poverty line (or twice poverty) are barely making ends meet, but they are not considered officially poor. When we talk here about the poverty level, then, keep in mind that we are talking only about official poverty and that there are many families and individuals living in near poverty who have trouble meeting their basic needs, especially when they face unusually high medical expenses, motor vehicle expenses, or the like. For this reason, many analysts think families need incomes twice as high as the federal poverty level just to get by (Wright, et. al., 2011). They thus use twice-poverty data (i.e., family incomes below twice the poverty line) to provide a more accurate understanding of how many Americans face serious financial difficulties, even if they are not living in official poverty.
The Extent of Poverty
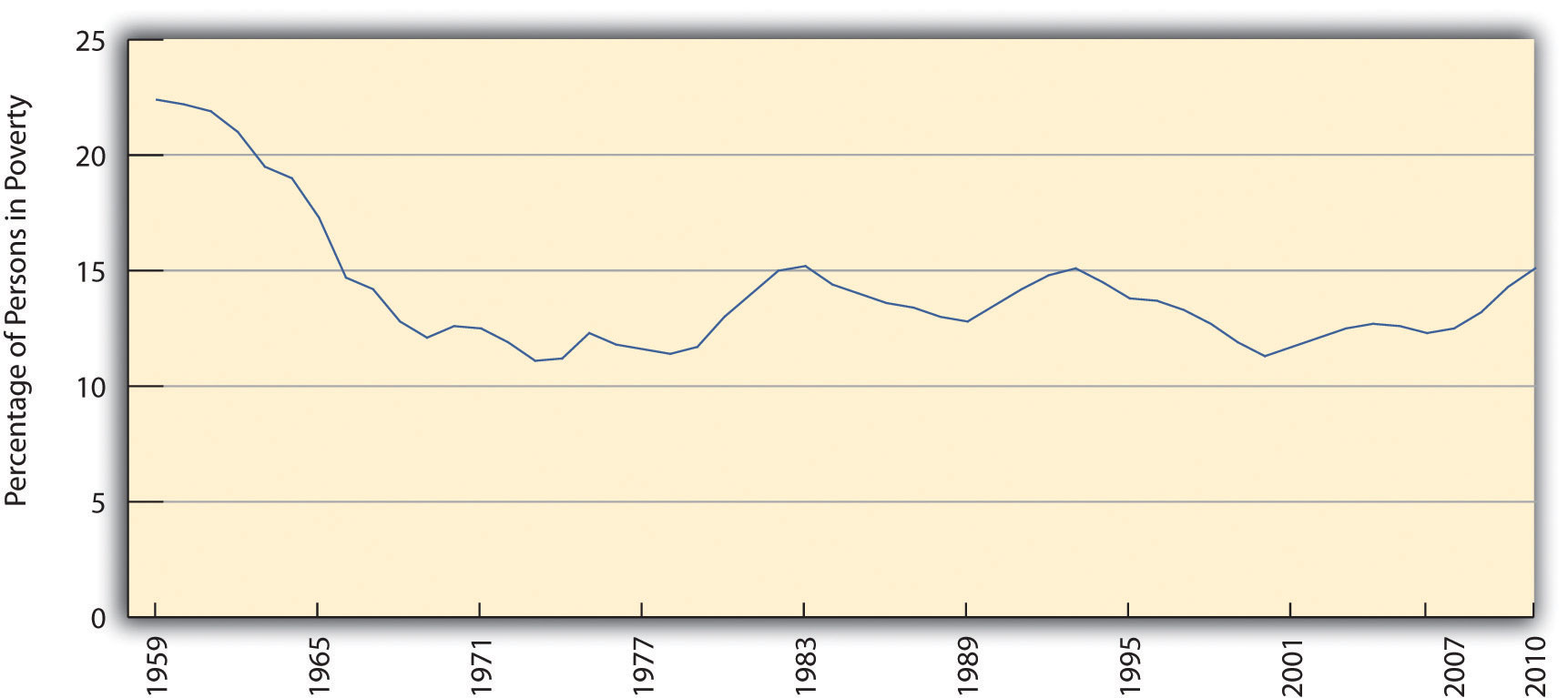
With this caveat in mind, how many Americans are poor? The US Census Bureau gives us some answers that use the traditional, official measure of poverty developed in 1963. In 2010, 15.1 percent of the US population, or 46.2 million Americans, lived in official poverty (DeNavas-Walt, et. al., 2011). This percentage represented a decline from the early 1990s but was higher than 2000 and even higher than the rate in the late 1960s (see Figure 2.1 “US Poverty, 1959–2010”). If we were winning the war on poverty in the 1960s (notice the sharp drop in the 1960s in Figure 2.1 “US Poverty, 1959–2010”), since then poverty has fought us to a standstill.
Figure 2.1 US Poverty, 1959–2010
Source: Data from US Census Bureau. (2011). Historical poverty tables: People. Retrieved from http://www.census.gov/hhes/www/poverty/data/historical/people.html.
Another way of understanding the extent of poverty is to consider episodic poverty, defined by the Census Bureau as being poor for at least two consecutive months in some time period. From 2004 to 2007, the last years for which data are available, almost one-third of the US public, equal to about 95 million people, were poor for at least two consecutive months, although only 2.2 percent were poor for all three years (DeNavas-Walt, et al., 2010). As these figures indicate, people go into and out of poverty, but even those who go out of it do not usually move very far from it. And as we have seen, the majority of Americans can expect to experience poverty or near poverty at some point in their lives.
The problems in the official poverty measure that were noted earlier have led the Census Bureau to develop a Supplemental Poverty Measure. This measure takes into account the many family expenses in addition to food; it also takes into account geographic differences in the cost of living, taxes paid and tax credits received, and the provision of food stamps, Medicaid, and certain other kinds of government aid. This new measure yields an estimate of poverty that is higher than the rather simplistic official poverty measure that, as noted earlier, is based solely on the size of a family and the cost of food and the amount of a family’s cash income. According to this new measure, the 2010 poverty rate was 16.0 percent, equal to 49.1 million Americans (Short, 2011). Because the official poverty measure identified 46.2 million people as poor, the new, more accurate measure increased the number of poor people in the United States by almost 3 million. Without the help of Social Security, food stamps, and other federal programs, at least 25 million additional people would be classified as poor (Sherman, 2011). These programs thus are essential in keeping many people above the poverty level, even if they still have trouble making ends meet and even though the poverty rate remains unacceptably high.
A final figure is worth noting. Recall that many poverty experts think that twice-poverty data—the percentage and number of people living in families with incomes below twice the official poverty level—are a better gauge than the official poverty level of the actual extent of poverty, broadly defined, in the United States. Using the twice-poverty threshold, about one-third of the US population, or more than 100 million Americans, live in poverty or near poverty (Pereyra, 2011). Those in near poverty are just one crisis—losing a job or sustaining a serious illness or injury—away from poverty. Twice-poverty data paint a very discouraging picture.
Key Takeaways
- The official poverty rate is based on the size of a family and a minimal food budget; this measure underestimates the true extent of poverty.
- The official poverty rate in 2010 was 15.1 percent, equal to more than 46 million Americans.
- About one-third of the US population, or more than 100 million Americans, have incomes no higher than twice the poverty line.
For Your Review
- Write a short essay that summarizes the problems by which the official poverty rate is determined.
- Sit down with some classmates and estimate what a family of four (two parents, two young children) in your area would have to pay annually for food, clothing, shelter, energy, and other necessities of life. What figure do you end up with? How does this sum of money compare with the official poverty line of $22,213 in 2010 for a family of four?
References
DeNavas-Walt, C., Proctor, B. D., & Smith, J. C. (2011). Income, poverty, and health insurance coverage in the United States: 2010 (Current Population Reports, P60-239). Washington, DC: US Census Bureau.
DeParle, J., Gebeloff, R., & Tavernise, S. (2011, November 4). Bleak portrait of poverty is off the mark, experts say. New York Times, p. A1.
Pereyra, L. (2011). Half in Ten campaign criticizes House Republican funding proposal. Washington, DC: Center for American Progress.
Sherman, A. (2011). Despite deep recession and high unemployment, government efforts—including the Recovery Act—prevented poverty from rising in 2009, new census data show. Washington, DC: Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
Short, K. (2011). The research supplemental poverty measure: 2010 (Current Population Reports, P60-241). Washington, DC: US Census Bureau.
Wright, V. R., Chau, M., & Aratani, Y. (2011). Who are America’s poor children? The official story. New York, NY: National Center for Children in Poverty.